This week's exercises had me doing a lot of experimentation! I definitely had to slow down and re-read the chapters and walk through the examples to get a good grasp on the strings and lists. At times, it was quite helpful to put pencil to paper to sketch out the processes in order to figure out how to get the program working. The best part of the exercises were the victory dances after finally getting the programs to work!
One real issue I ran into was running the code for the L-Systems. At times, it would lock up my desktop or I got a TimeLimitError: Program exceeded run time limit. on line ##. I ended up reducing the number of iterations in the code and switching to my Mac, which seemed to be able to handle the program better. Also, the text outputs were quite long for the L-Systems, so I provided only the image outputs.
Otherwise, a fun project!
String Exercises
6. Write a function that reverses its string argument.
# import testEqual function from test library
from test import testEqual
# define string argument
forwardstring = "reverse my string"
# define function that reverses string argument
def reverse(forwardstring):
backwardstring = ""
for char in forwardstring:
backwardstring = char + backwardstring
return backwardstring
# print reversed string
print(reverse(forwardstring))
# test reverse function
testEqual(reverse("happy"), "yppah")
testEqual(reverse("Python"), "nohtyP")
testEqual(reverse(""),"")
Output: (input string = "reverse my string")
gnirts ym esrever
Pass
Pass
Pass
7. Write a function that mirrors its argument.
# import testEqual function from test library
from test import testEqual
# define string argument
forwardstring = "mirror my string"
# define function that mirrors string argument
def mirror(forwardstring):
backwardstring = ""
for char in forwardstring:
backwardstring = char + backwardstring
return forwardstring + backwardstring
# print mirrored string
print(mirror(forwardstring))
# test mirror function
testEqual(mirror('good'),'gooddoog')
testEqual(mirror('Python'),'PythonnohtyP')
testEqual(mirror(''), '')
testEqual(mirror('a'),'aa')
Output: (input string = "mirror my string")
mirror my stringgnirts ym rorrim
Pass
Pass
Pass
Pass
11. Write a function that removes the first occurrence of a string from another string.
# import testEqual function from test library
from test import testEqual
# define string and substring arguments
inputstring = "Hello"
substring = "l"
# define function that removes the substring from the inputstring
def remove(substring, inputstring):
if substring not in inputstring:
return inputstring # return input string if substring not in inputstring
else:
locatesub = inputstring.find(substring) # get index for substring
sublength = len(substring) # get length of substring
redactedstring = inputstring[:locatesub] + inputstring[locatesub + sublength:] # construct redacted string
return redactedstring
# print redacted string
print(remove(substring, inputstring))
# test remove function
testEqual(remove('an', 'banana'),'bana')
testEqual(remove('cyc', 'bicycle'), 'bile')
testEqual(remove('iss', 'Mississippi'), 'Missippi')
testEqual(remove('egg', 'bicycle'), 'bicycle')
Output: (input string = "Hello", substring = "l")
Helo
Pass
Pass
Pass
Pass
12. Write a function that removes all occurences of a string from another string.
# import testEqual function from test library
from test import testEqual
# define inputstring and substring
inputstring = "Remove all substrings from string, even if string has lots of those substrings."
substring = "string"
# define function that removes all occurrences of substring from inputstring
def remove_all(substring,inputstring):
if substring not in inputstring:
return inputstring # return input string if substring not in inputstring
else:
subcount = inputstring.count(substring) # get number of substring occurrences
sublength = len(substring) # get length of substring
for i in range(subcount):
locatesub = inputstring.find(substring) # get index for substring
inputstring = inputstring[:locatesub] + inputstring[locatesub + sublength:] # construct redacted string
return inputstring
# print redacted string
print(remove_all(substring, inputstring))
# test remove_all function
testEqual(remove_all('an', 'banana'), 'ba')
testEqual(remove_all('cyc', 'bicycle'), 'bile')
testEqual(remove_all('iss', 'Mississippi'), 'Mippi')
testEqual(remove_all('eggs', 'bicycle'), 'bicycle')
Output: (input string = "Remove all substrings from string, even if string has lots of those substrings", substring = "string")
Remove all subs from , even if has lots of those subs.
Pass
Pass
Pass
Pass
15. Here is something called an arrowhead curve. Use 60 degrees.
import turtle
def createLSystem(numIters,axiom):
startString = axiom
endString = ""
for i in range(numIters):
endString = processString(startString)
startString = endString
return endString
def processString(oldStr):
newstr = ""
for ch in oldStr:
newstr = newstr + applyRules(ch)
return newstr
def applyRules(ch):
newstr = ""
if ch == 'X':
newstr = 'YF+XF+Y' # Rule 1
elif ch == 'Y':
newstr = 'XF-YF-X' # Rule 2
else:
newstr = ch # no rules apply so keep the character
return newstr
def drawLsystem(aTurtle,instructions,angle,distance):
for cmd in instructions:
if cmd == 'F':
aTurtle.forward(distance)
elif cmd == 'B':
aTurtle.backward(distance)
elif cmd == '+':
aTurtle.right(angle)
elif cmd == '-':
aTurtle.left(angle)
else:
print('Error:', cmd, 'is an unknown command')
def main():
inst = createLSystem(4,"YF") #create the string
print(inst)
t = turtle.Turtle() #create the turtle
wn = turtle.Screen()
t.up()
t.back(100)
t.down()
t.speed(9)
drawLsystem(t,inst,60,5) #draw the picture
#angle 60, segment length 5
wn.exitonclick()
main()
Output:
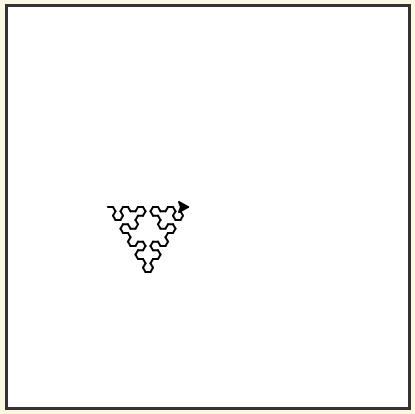
16. Try the Peano-Gosper curve. Use 60 degrees.
import turtle
def createLSystem(numIters,axiom):
startString = axiom
endString = ""
for i in range(numIters):
endString = processString(startString)
startString = endString
return endString
def processString(oldStr):
newstr = ""
for ch in oldStr:
newstr = newstr + applyRules(ch)
return newstr
def applyRules(ch):
newstr = ""
if ch == 'X':
newstr = 'X+YF++YF-FX--FXFX-YF+' # Rule 1
elif ch == 'Y':
newstr = '-FX+YFYF++YF+FX--FX-Y' # Rule 2
else:
newstr = ch # no rules apply so keep the character
return newstr
def drawLsystem(aTurtle,instructions,angle,distance):
for cmd in instructions:
if cmd == 'F':
aTurtle.forward(distance)
elif cmd == 'B':
aTurtle.backward(distance)
elif cmd == '+':
aTurtle.right(angle)
elif cmd == '-':
aTurtle.left(angle)
else:
print('Error:', cmd, 'is an unknown command')
def main():
inst = createLSystem(3,"FX") #create the string
print(inst)
t = turtle.Turtle() #create the turtle
wn = turtle.Screen()
t.up()
t.back(100)
t.down()
t.speed(9)
drawLsystem(t,inst,60,5) #draw the picture
#angle 60, segment length 5
wn.exitonclick()
main()
Output:

List Exercises
7. Write a function to count how many odd numbers are in a list.
# define list of numbers
numberlist = [0, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 16, 81]
# define function for odd number counter
def oddcount(numberlist):
oddlist = []
for value in numberlist:
if value % 2 != 0:
oddlist.append(value)
oddlistcount = len(oddlist)
return oddlistcount
# print odd number count
print(oddcount(numberlist))
Output: (input list = [0, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 16, 81])
7
8. Sum up all the even numbers in a list.
# define list of numbers
numberlist = [0, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12]
# define function for even number sum-er
def evensum(numberlist):
evenlist = []
for value in numberlist:
if value % 2 == 0:
evenlist.append(value)
evensum = sum(evenlist)
return evensum
# print sum of even numbers
print(evensum(numberlist))
Output: (input list = [0, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12])
40
9. Sum up all the negative numbers in a list.
# define list of numbers
numberlist = [-1, 3, -4, 5, 6, 7, -8, 10, 12]
# define function for negative number sum-er
def negsum(numberlist):
neglist = []
for value in numberlist:
if value < 1:
neglist.append(value)
negsum = sum(neglist)
return negsum
# print sum of negative numbers
print(negsum(numberlist))
Output: (input list = [-1, 3, -4, 5, 6, 7, -8, 10, 12])
-13
14. Write a function replace(s, old, new) that replaces all occurences of old with new in a string s:
# import testEqual
from test import testEqual
# define string, old substring, and new substring
s = "I love spom! Spom is my favorite food!"
old = "om"
new = "am"
# define replace function
def replace(s, old, new):
s_withoutold = s.split(old)
glue = new
s_new = glue.join(s_withoutold)
return(s_new)
# print modified script
print(replace(s, old, new))
# test replace function
testEqual(replace('Mississippi', 'i', 'I'), 'MIssIssIppI')
s = 'I love spom! Spom is my favorite food. Spom, spom, spom, yum!'
testEqual(replace(s, 'om', 'am'), 'I love spam! Spam is my favorite food. Spam, spam, spam, yum!')
testEqual(replace(s, 'o', 'a'), 'I lave spam! Spam is my favarite faad. Spam, spam, spam, yum!')
Output: (input string = "I love spom! Spom is my favorite food!", old string = "om", new string = "am")
I love spam! Spam is my favorite food!
Pass
Pass
Pass
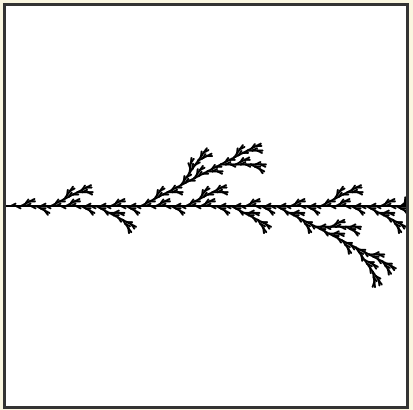
15. Here are the rules for an L-system that creates something that resembles a common garden herb. Implement the following rules and try it. Use an angle of 25.7 degrees.
import turtle
def createLSystem(numIters,axiom):
startString = axiom
endString = ""
for i in range(numIters):
endString = processString(startString)
startString = endString
return endString
def processString(oldStr):
newstr = ""
for ch in oldStr:
newstr = newstr + applyRules(ch)
return newstr
def applyRules(ch):
newstr = ""
if ch == 'H':
newstr = 'HFX[+H][-H]' # Rule 1
elif ch == 'X':
newstr = 'X[-FFF][+FFF]FX' # Rule 2
else:
newstr = ch # no rules apply so keep the character
return newstr
def drawLsystem(aTurtle,instructions,angle,distance):
savedInfoList = []
for cmd in instructions:
if cmd == 'F':
aTurtle.forward(distance)
elif cmd == 'B':
aTurtle.backward(distance)
elif cmd == '+':
aTurtle.right(angle)
elif cmd == '-':
aTurtle.left(angle)
elif cmd == '[':
savedInfoList.append([aTurtle.heading(),aTurtle.xcor(),aTurtle.ycor()])
print(savedInfoList)
elif cmd == ']':
newInfo = savedInfoList.pop()
aTurtle.setheading(newInfo[0])
aTurtle.setposition(newInfo[1],newInfo[2])
else:
print('Error:', cmd, 'is an unknown command')
def main():
inst = createLSystem(4,"H") #create the string
print(inst)
t = turtle.Turtle() #create the turtle
wn = turtle.Screen()
t.up()
t.back(200)
t.down()
t.speed(9)
drawLsystem(t,inst,27.5,8) #draw the picture
#angle 27.5, segment length 8
wn.exitonclick()
main()
Output:
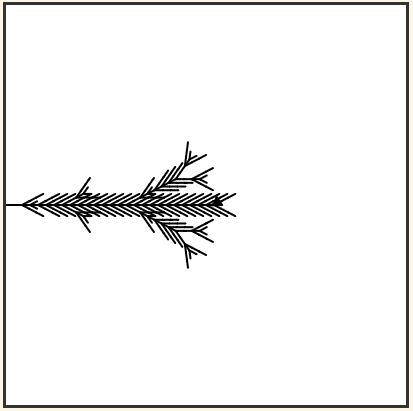
16. Here is another L-System. Use an Angle of 25.
import turtle
def createLSystem(numIters,axiom):
startString = axiom
endString = ""
for i in range(numIters):
endString = processString(startString)
startString = endString
return endString
def processString(oldStr):
newstr = ""
for ch in oldStr:
newstr = newstr + applyRules(ch)
return newstr
def applyRules(ch):
newstr = ""
if ch == 'F':
newstr = 'F[-F]F[+F]F' # Rule 1
else:
newstr = ch # no rules apply so keep the character
return newstr
def drawLsystem(aTurtle,instructions,angle,distance):
savedInfoList = []
for cmd in instructions:
if cmd == 'F':
aTurtle.forward(distance)
elif cmd == 'B':
aTurtle.backward(distance)
elif cmd == '+':
aTurtle.right(angle)
elif cmd == '-':
aTurtle.left(angle)
elif cmd == '[':
savedInfoList.append([aTurtle.heading(),aTurtle.xcor(),aTurtle.ycor()])
print(savedInfoList)
elif cmd == ']':
newInfo = savedInfoList.pop()
aTurtle.setheading(newInfo[0])
aTurtle.setposition(newInfo[1],newInfo[2])
else:
print('Error:', cmd, 'is an unknown command')
def main():
inst = createLSystem(4,"F") #create the string
print(inst)
t = turtle.Turtle() #create the turtle
wn = turtle.Screen()
t.up()
t.back(200)
t.down()
t.speed(9)
drawLsystem(t,inst,27.5,5) #draw the picture
#angle 25, segment length 5
wn.exitonclick()
main()
Output: